How to Build an Effective ISO 14001 Internal Audit Program
In addition to assessing conformance with the standard, the internal audit is used to assess conformance with other requirements, e.g., the EMS itself, various internal and compliance-required plans, corporate requirements (if they exist) and other standards to which the organization may subscribe.
Internal Audit Program
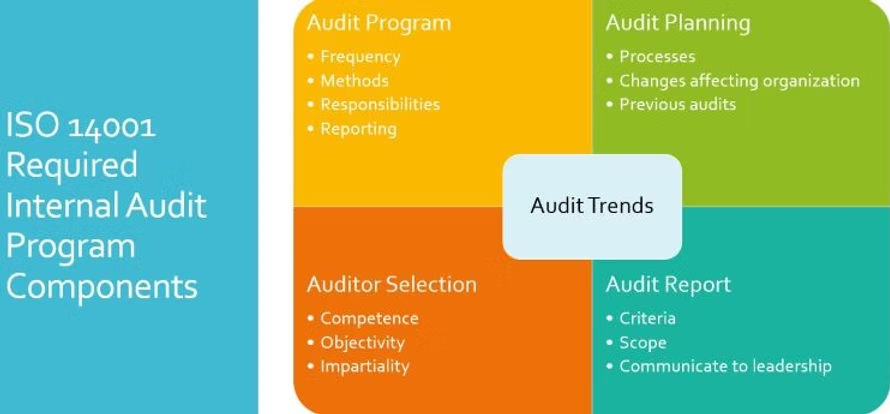
Under clause 9.2.2., the internal audit program must be documented and must spell out:
The frequency of internal audits
The methods used to conduct the internal audits
Responsibilities under the internal audit program
Planning for the internal audits, and
How internal audits will be reported
Processes of environmental importance, changes to the organization and the results of previous audits must also be considered.
In addition, each audit must include:
Defined audit criteria
Defined audit scope
Objectivity and impartiality of the auditors and the audit process
Reporting of the audit results to management
Auditor Competence & Objectivity
Be sure that the internal auditors are competent to conduct the audit, based on the appropriate education, training or experience (Clause 7.2).
If the organization cannot ensure the objectivity of the auditor or cannot demonstrate that the auditors have the necessary competency, they will have to go outside the immediate organization to conduct the internal audits – through other company entities or consultants, for example.
Need ISO Help? Check out our online store. Schedule a free consultation.
Results & Trending
If you never have findings during your internal audits but have findings during your registrar surveillance and recertification audits or agency inspections, it is likely your internal audit program is ineffective. Consider the changes you can make to people or processes to improve the audit process.
Do not confuse the internal audit with the evaluation of compliance (Clause 9.1.2). Internal audits assess conformance to the management system and compliance evaluations assess compliance with regulatory requirements.
Be sure and trend the results of internal audits for management review (Clause 9.3.d.4) and use the information in the audit planning process (Clause 9.2.2). This trending is frequently overlooked.
Conclusion
It’s all in the details. Make sure you have a copy of the standard and are using it to build and check your system. That way, there won’t be any surprises at your next surveillance or re-certification audit.
Need help? Check out our EMS forms and templates in our ISO Help Store, or schedule time for a one-on-one phone call with an ISO Auditor at our ISO Help Consult page.
Interested in more information on our comprehensive suite of environmental services? E-mail us to request a copy of our Statement of Qualifications.
About the Author
Joyce Kristiansson, M.S., is a Certified Environmental Professional Auditor and former registrar auditor for an ISO certification body. With more than 40 years of environmental experience, including fifteen years in ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems, Joyce has experienced EMS systems and processes from all perspectives: developing, maintaining, sustaining and auditing (both internal and certification). Recognizing the improved environmental performance and positive financial results that can result from an effective EMS, Joyce wants to make the process as simple and inexpensive as possible so that small and medium-sized businesses can have the same competitive advantages as larger companies – without using a consultant.